Hi Every One!!!!
Vcenter is used for maintaining the esx server from a centralized place with user permission and cluster creation and the licensing issues. while migration time from 4.0 to 4.1, we need to follow these steps for getting old database which is stored in 4.0 to 4.1.
Before migration All the service of vcenter should be stop
VMware VirtualCenter Server
VMware VirtualCenter Management Webservices
VMware vCenter Update Manager Service
Mount the vcenter in the old vcenter machine and open the cd and copy the Datamigration folder to C:\Datamigration
Extract all the file in the same folder
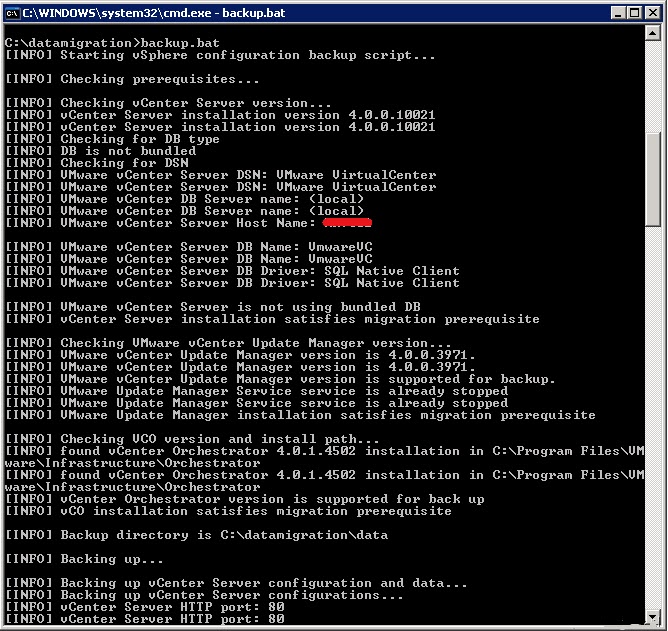
Navigate to C:\Datamigration\ and run backup.bat , the script will backup all configuration settings from your recent vCenter installation and database. (Software builds, used ports, database information, server names and VUM Settings/Patches etc.).. once finished all the important data is stored in C:\Datamigration\Data\
If there are any errors while making the backup… check this and fix before you go further!
Now you need to copy the C:\Databasemigration\ folder to your new planned vCenter 4.1 server. You can do this by share, copy this on USB stick or whatever.
Migrate the database and install vCenter 4.1:
- Login to the new vCenter server;
- Mount the new VMware vCenter Server 4.1 and modules
Open CMD:
- Navigate to C:\Data migration\ and run install.bat. The script will check if the correct data is present..
If you used a different name for your new vCenter server press Yes.. to continue
Then you must select the vCenter 4.1 and VUM installation source. In my case the mounted ISO has driveletter F:\
The configuration will be validated, correct ports numbers, vCenter serial number etc.. all good..
.. The vCenter Installation is started
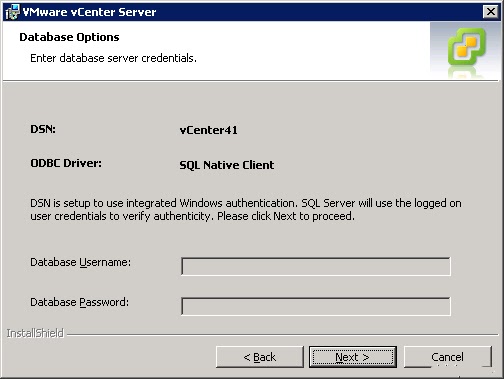
I already installed a Microsoft SQL 2005 Enterprise server (local) and created a 32 bit ODBC connection, THEN select “vCenter41” DSN
If needed, give the correct credentials
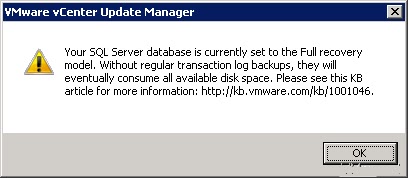
You can modify this later, please check: http://kb.vmware.com/kb/1001046 for more information
- I changed the installation path to D:\Program Files\VMware\Infrastructure\ .. default location is C:\..\.
Oke, the installation was not so difficult. After clicking finish the install.bat will continue with the VMware Update Manager database migration and installation.
VMware Update Manager – Database migration and installation software:
As you can see “vCenter Server migration installed completed successfully” great
The install.bat script will continue and check again if the selected VUM ports are available and if the copied data migratable is for the new VUM database location
For VMware Update Manager you need to create a 64-Bit DSN. You can create this here: C:\WINDOWS\SysWOW64\odbcad32.exe .. oke, thats done.. select the VUM (already created before installation) database.
The installation and patch download location is by default C:\.. I prefer to install this data on a separate disk.. so I changed the installation path to D:\…\..
Now you can connect your vCenter server and manage your hosts and VM’s.. sometimes you can’t!
Tip before connect the vCenter:
- Reboot your new vCenter 4.1 server;
- On the ESX host: Restart your management services: service mgmt-vmware restart
- On the ESX host: Use a text editor to view/change the IP address inside the xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx tags the following file:/etc/opt/vmware/vpxa/vpxa.cfg
Finally result:
Successful migration process of vCenter 4.0 to new 4.1 server
I Hope Every Body Enjoyed .Problem has been solved !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!